作者:sunshine小小倩
转发链接:https://juejin.im/post/592d4a5b0ce463006b43b6da
一个好的程序员肯定是要能书写可掩护的代码,而不是一次性的代码,怎么能让团队当中其他人乃至一段韶光时候你再看你某个时候写的代码也能看懂呢,这就须要规范你的代码了。我是有一点强制症的人,上周我们后端给我了一个CanUsename的接口(该接口的目的是判断输入的目的地是否是4级目的地),我真的是崩溃的。我只是以为这个名字不足语义化,但是让我自己想一个名字我又想不出来,于是我就在想,如果有一套命名规范的话,那么往后起名字就不用发愁了,直接按照规范来就好了
不推举:
<script src="http://cdn.com/foundation.min.js"></script>复制代码
推举
<script src="//cdn.com/foundation.min.js"></script>复制代码变量命名
命名办法 : 小驼峰式命名方法命名规范 : 类型+工具描述的办法,如果没有明确的类型,就可以使前缀为名词
推举
var tableTitle = "LoginTable"复制代码
不推举
var getTitle = "LoginTable"复制代码函数
命名办法 : 小驼峰办法 ( 布局函数利用大驼峰命名法 )命名规则 : 前缀为动词
推举:
//是否可阅读function canRead(){ return true;}//获取姓名function getName{ return this.name}复制代码常量
命名方法 : 全部大写命名规范 : 利用大写字母和下划线来组合命名,下划线用以分割单词。推举:
var MAX_COUNT = 10; var URL = 'http://www.baidu.com';复制代码类的成员公共属性和方法 : 同变量命名办法私有属性和方法 : 前缀为下划线(_)后面跟公共属性和方法一样的命名办法
推举(将name换成this是不是更熟习了呢)
function Student(name) { var _name = name; // 私有成员 // 公共方法 this.getName = function () { return _name; } // 公共办法 this.setName = function (value) { _name = value; }}var st = new Student('tom');st.setName('jerry');console.log(st.getName()); // => jerry:输出_name私有变量的值复制代码注释规范单行注释 ( // )单独一行://(双斜线)与注释笔墨之间保留一个空格在代码后面添加注释://(双斜线)与代码之间保留一个空格,并且//(双斜线)与注释笔墨之间保留一个空格。注释代码://(双斜线)与代码之间保留一个空格。
推举 :
// 调用了一个函数;1)单独在一行setTitle();var maxCount = 10; // 设置最大量;2)在代码后面注释// setName(); // 3)注释代码复制代码多行注释 ( / 注释解释 / )若开始(/和结束(/)都在一行,推举采取单行注释若至少三行注释时,第一行为/,末了行为/,其他行以开始,并且注释笔墨与保留一个空格。推举 : / 代码实行到这里后会调用setTitle()函数 setTitle():设置title的值 / setTitle();复制代码函数 ( 方法 ) 注释
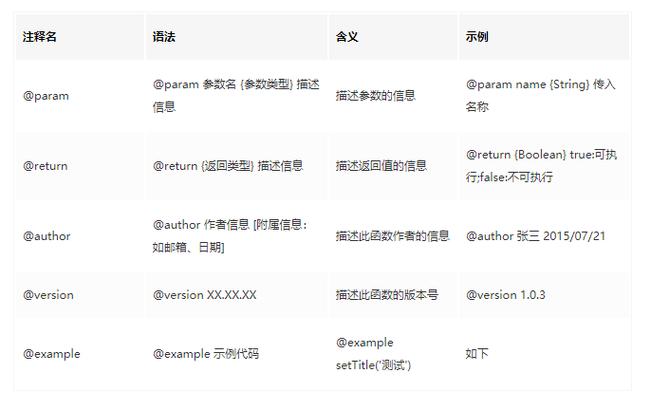
函数(方法)注释也是多行注释的一种,但是包含了分外的注释哀求,参照 javadoc(百度百科)语法:
/ 函数解释 @关键字 /复制代码
常用注释关键字
推举 :
/ - 合并Grid的行 - @param grid {Ext.Grid.Panel} 须要合并的Grid - @param cols {Array} 须要合并列的Index(序号)数组;从0开始计数,序号也包含。 - @param isAllSome {Boolean} :是否2个tr的cols必须完成一样才能进行合并。true:完成一样;false(默认):不完备一样 - @return void - @author polk6 2015/07/21 - @example - _________________ _________________ - | 年事 | 姓名 | | 年事 | 姓名 | - ----------------- mergeCells(grid,[0]) ----------------- - | 18 | 张三 | => | | 张三 | - ----------------- - 18 --------- - | 18 | 王五 | | | 王五 | - ----------------- -----------------/function mergeCells(grid, cols, isAllSome) { // Do Something}复制代码HTML规范文档规范
利用 HTML5 的文档声明类型 : <!DOCTYPE html>
DOCTYPE标签是一种标准通用标记措辞的文档类型声明,它的目的是要见告标准通用标记措辞解析器,它该当利用什么样的文档类型定义(DTD)来解析文档。利用文档声明类型的浸染是为了防止开启浏览器的怪异模式。没有DOCTYPE文档类型声明会开启浏览器的怪异模式,浏览器会按照自己的解析办法渲染页面,在不同的浏览器下面会有不同的样式。如果你的页面添加了<!DOCTYP>那么,那么就等同于开启了标准模式。浏览器会按照W3C标准解析渲染页面。脚本加载说到js和css的位置,大家该当都知道js放不才面,css放在上面。但是,如果你的项目只须要兼容ie10+或者只是在移动端访问,那么可以利用HTML5的新属性async,将脚本文件放在<head>内兼容老旧浏览器(IE9-)时:脚本引用写在 body 结束标签之前,并带上 async 属性。这虽然在老旧浏览器中不会异步加载脚本,但它只壅塞了 body 结束标签之前的 DOM 解析,这就大大降落了其壅塞影响。而在当代浏览器中:脚本将在 DOM 解析器创造 body 尾部的 script 标签才进行加载,此时加载属于异步加载,不会壅塞 CSSOM(但其实行仍发生在 CSSOM 之后)。综上所述,所有浏览器中推举:
<html> <head> <link rel="stylesheet" href="main.css"> </head> <body> <!-- body goes here --> <script src="main.js" async></script> </body></html>复制代码
只兼容当代浏览器推举:
<html> <head> <link rel="stylesheet" href="main.css"> <script src="main.js" async></script> </head> <body> <!-- body goes here --> </body></html>复制代码语义化
我们一贯都在说语义化编程,语义化编程,但是在代码中很少有人完备利用精确的元素。利用语义化标签也是有情由SEO的。
语义化是指:根据元素其被创造出来时的初始意义来利用它。意思便是用精确的标签干精确的事,而不是只有div和span。
不推举:
<b>My page title</b><div class="top-navigation"> <div class="nav-item"><a href="#home">Home</a></div> <div class="nav-item"><a href="#news">News</a></div> <div class="nav-item"><a href="#about">About</a></div></div><div class="news-page"> <div class="page-section news"> <div class="title">All news articles</div> <div class="news-article"> <h2>Bad article</h2> <div class="intro">Introduction sub-title</div> <div class="content">This is a very bad example for HTML semantics</div> <div class="article-side-notes">I think I'm more on the side and should not receive the main credits</div> <div class="article-foot-notes"> This article was created by David <div class="time">2014-01-01 00:00</div> </div> </div> <div class="section-footer"> Related sections: Events, Public holidays </div> </div></div><div class="page-footer"> Copyright 2014</div>复制代码
推举
html 代码:<!-- The page header should go into a header element --><header> <!-- As this title belongs to the page structure it's a heading and h1 should be used --> <h1>My page title</h1></header><!-- All navigation should go into a nav element --><nav class="top-navigation"> <!-- A listing of elements should always go to UL (OL for ordered listings) --> <ul> <li class="nav-item"><a href="#home">Home</a></li> <li class="nav-item"><a href="#news">News</a></li> <li class="nav-item"><a href="#about">About</a></li> </ul></nav><!-- The main part of the page should go into a main element (also use role="main" for accessibility) --><main class="news-page" role="main"> <!-- A section of a page should go into a section element. Divide a page into sections with semantic elements. --> <section class="page-section news"> <!-- A section header should go into a section element --> <header> <!-- As a page section belongs to the page structure heading elements should be used (in this case h2) --> <h2 class="title">All news articles</h2> </header> <!-- If a section / module can be seen as an article (news article, blog entry, products teaser, any other re-usable module / section that can occur multiple times on a page) a article element should be used --> <article class="news-article"> <!-- An article can contain a header that contains the summary / introduction information of the article --> <header> <!-- As a article title does not belong to the overall page structure there should not be any heading tag! --> <div class="article-title">Good article</div> <!-- Small can optionally be used to reduce importance --> <small class="intro">Introduction sub-title</small> </header> <!-- For the main content in a section or article there is no semantic element --> <div class="content"> <p>This is a good example for HTML semantics</p> </div> <!-- For content that is represented as side note or less important information in a given context use aside --> <aside class="article-side-notes"> <p>I think I'm more on the side and should not receive the main credits</p> </aside> <!-- Articles can also contain footers. If you have footnotes for an article place them into a footer element --> <footer class="article-foot-notes"> <!-- The time element can be used to annotate a timestamp. Use the datetime attribute to specify ISO time while the actual text in the time element can also be more human readable / relative --> <p>This article was created by David <time datetime="2014-01-01 00:00" class="time">1 month ago</time></p> </footer> </article> <!-- In a section, footnotes or similar information can also go into a footer element --> <footer class="section-footer"> <p>Related sections: Events, Public holidays</p> </footer> </section></main><!-- Your page footer should go into a global footer element --><footer class="page-footer"> Copyright 2014</footer>复制代码alt标签不为空
<img>标签的 alt 属性指定了替代文本,用于在图像无法显示或者用户禁用图像显示时,代替图像显示在浏览器中的内容。假设由于下列缘故原由用户无法查看图像,alt 属性可以为图像供应替代的信息:
网速太慢src 属性中的缺点浏览器禁用图像用户利用的是屏幕阅读器从SEO角度考虑,浏览器的爬虫爬不到图片的内容,以是我们要有笔墨见告爬虫图片的内容
构造、表现、行为三者分离只管即便在文档和模板中只包含构造性的 HTML;而将所有表现代码,移入样式表中;将所有动作行为,移入脚本之中。在此之外,为使得它们之间的联系尽可能的小,在文档和模板中也只管即便少地引入样式和脚本文件。建议:
不该用超过一到两张样式表不该用超过一到两个脚本(学会用合并脚本)不该用行内样式(<style>.no-good {}</style>)不在元素上利用 style 属性(<hr style="border-top: 5px solid black">)不该用行内脚本(<script>alert('no good')</script>)不该用表象元素(i.e. <b>, <u>, <center>, <font>, <b>)不该用表象 class 名(i.e. red, left, center)HTML只关注内容HTML只显示展示内容信息不要引入一些特定的 HTML 构造来办理一些视觉设计问题不要将img元素当做专门用来做视觉设计的元素样式上的问题该当利用css办理不推举:
<!-- We should not introduce an additional element just to solve a design problem --><span class="text-box"> <span class="square"></span> See the square next to me?</span>css 代码:.text-box > .square { display: inline-block; width: 1rem; height: 1rem; background-color: red;}复制代码
推举
html 代码:<!-- That's clean markup! --><span class="text-box"> See the square next to me?</span>css 代码:/ We use a :before pseudo element to solve the design problem of placing a colored square in front of the text content /.text-box:before { content: ""; display: inline-block; width: 1rem; height: 1rem; background-color: red;}复制代码
图片和 SVG 图形能被引入到 HTML 中的唯一情由是它们呈现出了与内容干系的一些信息。
不推举
html 代码:<!-- Content images should never be used for design elements! --><span class="text-box"> <img src="square.svg" alt="Square" /> See the square next to me?</span>复制代码
推举
html 代码:<!-- That's clean markup! --><span class="text-box"> See the square next to me?</span>css 代码:/ We use a :before pseudo element with a background image to solve the problem /.text-box:before { content: ""; display: inline-block; width: 1rem; height: 1rem; background: url(square.svg) no-repeat; background-size: 100%;}复制代码js规范避免全局命名空间污染
防止全局命名空间被污染,我们常日的做法是将代码包裹成一个 IIFE(Immediately-Invoked Function Expression),创建独立隔绝的定义域。也使得内存在实行完后立即开释。
IIFE 还可确保你的代码不会轻易被其它全局命名空间里的代码所修正(i.e. 第三方库,window 引用,被覆盖的未定义的关键字等等)。不推举:
var x = 10, y = 100;// Declaring variables in the global scope is resulting in global scope pollution. All variables declared like this// will be stored in the window object. This is very unclean and needs to be avoided.console.log(window.x + ' ' + window.y);复制代码
推举
// We declare a IIFE and pass parameters into the function that we will use from the global space(function(log, w, undefined){ 'use strict'; var x = 10, y = 100; // Will output 'true true' log((w.x === undefined) + ' ' + (w.y === undefined));}(window.console.log, window));复制代码
推举的IIFE写法:
(function(){ 'use strict'; // Code goes here}());复制代码
如果你想引用全局变量或者是外层 IIFE 的变量,可以通过下列办法传参:
(function($, w, d){ 'use strict'; $(function() { w.alert(d.querySelectorAll('div').length); });}(jQuery, window, document));复制代码严格模式
ECMAScript 5 严格模式可在全体脚本或独个方法内被激活。它对应不同的 javascript 语境会做更加严格的缺点检讨。严格模式也确保了 javascript 代码更加的健壮,运行的也更加快速。
严格模式会阻挡利用在未来很可能被引入的预留关键字。
你该当在你的脚本中启用严格模式,最好是在独立的 IIFE 中运用它。避免在你的脚本第一行利用它而导致你的所有脚本都启动了严格模式,这有可能会引发一些第三方类库的问题。
变量声明总是利用 var 来声明变量。如不指定 var,变量将被隐式地声明为全局变量,例如
var a = b = 0; //b会被隐式的创建为全局变量复制代码
以是,请总是利用 var 来声明变量,并且利用单var模式(将所有的变量在函数最前面只利用一个var定义)。例如:
(function (){ 'use strict' var a = 0, b = 0, c = 0, i, j, myObject();}())复制代码
采取严格模式带来的好处是,当你手误输入缺点的变量名时,它可以通过报错信息来帮助你定位缺点出处。
js声明提前javascript会自动将函数浸染域内的变量和方法的定义提前(只是提前声明,赋值还是在原处)例如:
(function(log){ 'use strict'; var a = 10; for(var i = 0; i < a; i++) { var b = i i; log(b); } if(a === 10) { var f = function() { log(a); }; f(); } function x() { log('Mr. X!'); } x();}(window.console.log));复制代码
提升后的js
(function(log){ 'use strict'; // All variables used in the closure will be hoisted to the top of the function var a, i, b, f; // All functions in the closure will be hoisted to the top function x() { log('Mr. X!'); } a = 10; for(i = 0; i < a; i++) { b = i i; log(b); } if(a === 10) { // Function assignments will only result in hoisted variables but the function body will not be hoisted // Only by using a real function declaration the whole function will be hoisted with its body f = function() { log(a); }; f(); } x();}(window.console.log));复制代码利用严格等
总是利用 === 精确的比较操作符,避免在判断的过程中,由 JavaScript 的逼迫类型转换所造成的困扰。例如:
(function(log){ 'use strict'; log('0' == 0); // true log('' == false); // true log('1' == true); // true log(null == undefined); // true var x = { valueOf: function() { return 'X'; } }; log(x == 'X');}(window.console.log));复制代码等同== 和严格等===的差异==, 两边值类型不同的时候,要前辈行类型转换,再比较。===,不做类型转换,类型不同的一定不等。
==等同操作符
如果两个值具有相同类型,会进行===比较,返回===的比较值如果两个值不具有相同类型,也有可能返回true如果一个值是null另一个值是undefined,返回true如果一个值是string另个是number,会把string转换成number再进行比较如果一个值是true,会把它转成1再比较,false会转成0console.log( false == null ) // falseconsole.log( false == undefined ) // falseconsole.log( false == 0 ) // trueconsole.log( false == '' ) // trueconsole.log( false == NaN ) // falseconsole.log( null == undefined ) // trueconsole.log( null == 0 ) // falseconsole.log( null == '' ) // falseconsole.log( null == NaN ) // falseconsole.log( undefined == 0) // falseconsole.log( undefined == '') // falseconsole.log( undefined == NaN) // falseconsole.log( 0 == '' ) // trueconsole.log( 0 == NaN ) // false复制代码
总结一下==
false 除了和自身比较为 true 外,和 0,"" 比较也为 truenull 只和 undefined 比较时为 true, 反过来 undefined 也仅和 null 比较为 true,没有第二个0 除了和 false 比较为 true,还有空字符串 ''" 和空数组 []空字符串 '' 除了和 false 比较为 true,还有一个数字 0==, >, <, +, -, ... 这些操作符所造成的隐式类型转换都是无副浸染的,它不会改变变量本身保存的值。,但是,如果你覆写某个工具的 valueOf/toString的话,==就会产生副浸染.
例如:
Array.prototype.valueOf = function() { this[0]++; return this;}var x = [1, 2, 3];x == 0;console.log(x); // [2, 2, 3]复制代码
===操作符:
假如两个值类型不同,返回false假如两个值都是number类型,并且数值相同,返回true假如两个值都是stirng,并且两个值的String内容相同,返回true假如两个值都是true或者都是false,返回true假如两个值都是指向相同的Object,Arraya或者function,返回true假如两个值都是null或者都是undefined,返回true真假判断js中以下内容为假:falsenullundefined0'' (空字符串)NaN设置默认参数辑操作符 || 和 && 也可被用来返回布尔值。如果操为难刁难象为非布尔工具,那每个表达式将会被自左向右地做真假判断。基于此操作,终极总有一个表达式被返回回来。这在变量赋值时,是可以用来简化你的代码的。例如:如果x不存在且y不存在,x=1;如果x存在y存在,x = y
if(!x) { if(!y) { x = 1; } else { x = y; }}复制代码
等同于:
x = x || y || 1;复制代码
这一小技巧常常用来给方法设定默认的参数。
(function(log){ 'use strict'; function multiply(a, b) { a = a || 1; b = b || 1; log('Result ' + a b); } multiply(); // Result 1 multiply(10); // Result 10 multiply(3, NaN); // Result 3 multiply(9, 5); // Result 45}(window.console.log));复制代码不该用eval()函数
就如eval的字面意思来说,恶魔,利用eval()函数会带来安全隐患。eval()函数的浸染是返回任意字符串,当作js代码来处理。
this关键字只在工具布局器、方法和在设定的闭包中利用 this 关键字。this 的语义在此有些误导。它时而指向全局工具(大多数时),时而指向调用者的定义域(在 eval 中),时而指向 DOM 树中的某一节点(当用事宜处理绑定到 HTML 属性上时),时而指向一个新创建的工具(在布局器中),还时而指向其它的一些工具(如果函数被 call() 和 apply() 实行和调用时)。
正由于它是如此随意马虎地被搞错,请限定它的利用场景:
在布局函数中在工具的方法中(包括由此创建出的闭包内)首选函数式风格函数式编程让你可以简化代码并缩减掩护本钱,由于它随意马虎复用,又适当地解耦和更少的依赖。
接下来的例子中,在一组数字求和的同一问题上,比较了两种办理方案。第一个例子是经典的程序处理,而第二个例子则是采取了函数式编程和 ECMA Script 5.1 的数组方法。不推举
(function(log){ 'use strict'; var arr = [10, 3, 7, 9, 100, 20], sum = 0, i; for(i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { sum += arr[i]; } log('The sum of array ' + arr + ' is: ' + sum)}(window.console.log));复制代码
推举(函数式编程):
(function(log){ 'use strict'; var arr = [10, 3, 7, 9, 100, 20]; var sum = arr.reduce(function(prevValue, currentValue) { return prevValue + currentValue; }, 0); log('The sum of array ' + arr + ' is: ' + sum);}(window.console.log));复制代码修正内建工具的原型链
修正内建的诸如 Object.prototype 和 Array.prototype 是被严厉禁止的。修正其它的内建工具比如 Function.prototype,虽危害没那么大,但始终还是会导致在开拓过程中难以 debug 的问题,应该也要避免。
三元条件判断(if 的快捷方法)用三元操作符分配或返回语句。在比较大略的情形下利用,避免在繁芜的情形下利用。没人乐意用 10 行三元操作符把自己的脑筋绕晕。不推举:
if(x === 10) { return 'valid';} else { return 'invalid';}复制代码
推举:
return x === 10 ? 'valid' : 'invalid'复制代码JSHint
在js规范中,有很多规范都是样式上的规范而不是逻辑上的规范,比如只管即便利用===而不是==,我们可以利用JSHint或者JSLint,Javascript代码验证工具,这种工具可以检讨你的代码并供应干系的代码改进见地。我个人利用的是JSHint,以是就以这个为例
webstorm内置JSHint对付ws爱好者来说,我没有用过其他的编译器,ws基本上能知足你的所有需求(最新的ws集成了vue)。在Settings => language & frameworks => JavaScript => Code Quality Tolls => JSHint
webstorm中的jshint
这些规范都是什么意思呢,这里列出一些常用的,剩下的大家可以参考官方文档
css规范id和class的命名ID和class的名称总是利用可以反应元素目的和用场的名称,或其他通用的名称,代替表象和晦涩难懂的名称不推举 :
.fw-800 { font-weight: 800;}.red { color: red;}复制代码
推举 :
.heavy { font-weight: 800;}.important { color: red;}复制代码合理的利用ID
一样平常情形下ID不应该被用于样式,并且ID的权重很高,以是不该用ID办理样式的问题,而是利用class不推举:
#content .title { font-size: 2em;}复制代码
推举:
.content .title { font-size: 2em;}复制代码css选择器中避免利用标署名
从构造、表现、行为分离的原则来看,该当只管即便避免css中涌现HTML标签,并且在css选择器中涌现标署名会存在潜在的问题。
利用子选择器很多前端开拓职员写选择器链的时候不该用 直接子选择器(注:直接子选择器和后代选择器的差异)。有时,这可能会导致疼痛的设计问题并且有时候可能会很耗性能。然而,在任何情形下,这是一个非常不好的做法。如果你不写很通用的,须要匹配到DOM末端的选择器, 你该当总是考虑直接子选择器。不推举:
.content .title { font-size: 2rem;}复制代码
推举
.content > .title { font-size: 2rem;}复制代码只管即便利用缩写属性
只管即便利用缩写属性对付代码效率和可读性是很有用的,比如font属性。不推举:
border-top-style: none;font-family: palatino, georgia, serif;font-size: 100%;line-height: 1.6;padding-bottom: 2em;padding-left: 1em;padding-right: 1em;padding-top: 0;复制代码
推举:
border-top: 0;font: 100%/1.6 palatino, georgia, serif;padding: 0 1em 2em;复制代码0后面不带单位
省略0后面的单位,不推举:
padding-bottom: 0px;margin: 0em;复制代码
推举:
padding-bottom: 0;margin: 0;复制代码属性情式为了担保同等性和可扩展性,每个声明该当用分号结束,每个声明换行。属性名的冒号后利用一个空格。出于同等性的缘故原由,属性和值(但属性和冒号之间没有空格)的之间始终利用一个空格。每个选择器和属性声明总是利用新的一行。属性选择器或属性值用双引号(””),而不是单引号(”)括起来。URI值(url())不要利用引号。
作为最佳实践,我们该当遵照以下顺序(该当按照下表的顺序):
构造性属性:
displayposition, left, top, right etc.overflow, float, clear etc.margin, padding表现性属性:
background, border etc.font, text不推举:
.box { font-family: 'Arial', sans-serif; border: 3px solid #ddd; left: 30%; position: absolute; text-transform: uppercase; background-color: #eee; right: 30%; isplay: block; font-size: 1.5rem; overflow: hidden; padding: 1em; margin: 1em;}复制代码
推举:
.box { display: block; position: absolute; left: 30%; right: 30%; overflow: hidden; margin: 1em; padding: 1em; background-color: #eee; border: 3px solid #ddd; font-family: 'Arial', sans-serif; font-size: 1.5rem; text-transform: uppercase;}
作者:sunshine小小倩转发链接:https://juejin.im/post/592d4a5b0ce463006b43b6da









